3. Physical structure(inorganic)
1)
Bedding structure
①
horizontal bedding
:
lake, beach, deep marine - parallel, continuous rather uniform, monotonous
ⓐ
rhythmites
thin,
repetitious sequence(cyclic) - texture, composition 의 교호
*
seasonal charge (varve) - glacial lake
*
beach bed - uprush and backwash (grain size, composition)
ⓑ
upper flow plane bed or flat bed (no movement of sediment)
fluvial
- braided, alluvial fans, glacial outwash
→sand,
gravel horizontal bedding for a few meter scale.
②
Bedforms and their internal stratification
ⓐ
current - generated structure (lower flow regime)
*
foreset stratification : influenced by sediment texture, velocity, bed shear stress.
by depth ratio
→
angular contact (increasing depth, increasing suspension load) → tangential →
concave
*
plan view
―――――――――――
increasing flow strength ――――――――→
linear
→ undulatory → cuspate → rhomboid(planed off) → flat bed
|
|
Ripple
|
Megaripple(dune)
|
Sandwave
|
|
Spacing
|
〈
60cm
|
60cm-6m
|
〉
6m
|
|
Height/Spacing
|
variable
|
large
|
small
|
|
Flow
velocity
|
low
(25~50cm/s)
|
high
(70~150cm/s)
|
moderate
(40~80cm/s)
|
|
Geometry
|
high
variable
|
high
variable
|
straight
to sinous
|
*
trough cross-bedding ← lenticular & trough shaped sets의 측방 이동 누적에
의해 형성.
*
tabular cross-bedding ← linear bedforms의 수평적 이동 누적에 의해 형성
◎
Reactivation surface : interruption in migration or erosional surface.
caused
by flow rates, tidal stage, tidal current direction
*
Climbing ripple cross-stratification : 다량의 부유 퇴적물 유입
(ripple
in drift): 측방 이동 + 상향 누적
(ripple
in phase: 주로 상향 누적 by rapid sediment input)
*
Hummocky cross-stratification
low-angle
and gently undulation cross-stratification
(dip
: 3~6°)
wavelength
: ~ a few meters
height
: up to 30~40cm (보통 수 centimeter)
caused
by storm waves on shelf
ⓑ
current - generated structures (upper flow regime)
*
upper plane bed
*
antidune - stream, tidal inlet, gentle-sloping beach
(line-crested) → low preservation
(뒤따르는
waning flow에 의해 대개 상쇄되어 보존 가능성은 낮음)
ⓒ
wave - generated structures
wave ripples : symmetrical (peak-crest, round-trough)
-
wave ripple crest - straight/slightly sinuous with common bifurcations
-
wave ripple - chevronlike cross-stratification
controlled
by wave size, grain size, wave period, depth of water
*
ripple index (R.I.) : ripple length/height
*
ripple symmetry index (R.S.I.) : length of horizontal projection of
(R.S.I.) (
2.5 〈 current ripple )
(
2.5 〉 wave ripple )
(R.I.) (
0~4 wave ripple )
(
15〈 current ripple )
ⓓ
other bedding type
①
flaser and lenticular bedding : tidal, streams, intertidal beach
altermating
of energy 또는 sand mud availability
┌ flaser : thin mud + sand - 비교적 high energy
└ lenticular : discontinuous sand lens - 비교적 low energy
②
wavy bedding : continuous mud (undulating)
③
graded bedding (inverse drading) : a few centimeters
- distribution grading - no fine in lower part
- coarse-tail grading - all size but grading in only coarse part
*
by turbidy currents, shallow water, intertidal - sudden decrease of competence
flooding (waning) 또는 hurricanes에 의해 형성 가능
④
imbrication and internal fabric
*
preferred orientation by gravitational field with current flow
: gravel, fossils on bedding surface
*imbrication
: overlapping arrangement → dip current 지시
: long axes parallel to flow
normal to flow : rolling of clasts in bed load
*
parting lineation : thin sandstone → flow parallel to lineation
2)
Bedding plane structure
(1)
Bottom mark (sole mark) : 퇴적층 층리면 하부에 imprint로서 보존,
상하 퇴적층은 조직이
상이함
: by current and gravity
ⓐ
flute or flute cast - by current (sediment accumulation : rapid high turbulent
flow)
up 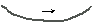 down stream
down stream
turbidite에서
많이 산출
indicator
of current direction and paleoslope
ⓑ
scour mark(transverse)
-
ridgelike transverse to paleocurrent direction
-
a few cm in scale
ⓒ
flute rill mark : long, narrow scour(anastomosing shape)
parallel
to current direction (tidal flat에서 형성)
ⓓ
longitudinal furrows and ridges
: straight, long, spaced closed ridge and furrows
ⓔ
tool mark : by downcurrent transport of pebbles, shells, twigs, branches, fishbone
* Groove cast (striation cast) : linear 긁힘(물체에 의해
파인 흔적)
* Brush marks
* Skip casts
* Chevron marks
* Prod marks
* Bounce marks
(2)
Surface marks : all not related to current
a
few millimeter ~ a centimeter in scale
①
current generation features
* current crescents (obstacle mark) : 장애물 주위에 생기는
구조
(stream,
foreshore beach, tidal flat 환경)
* sand shadows : aeolian setting 의 current crescents
(
low preservation )
* rill marks : small, bifurcation dendritic erosional feature
(
low preservation )
②
climate - related features
* raindrop impressions : mud or muddy sand surface
(a few millimeter) - arid, semiarid.
(not always symmetric <by falling oblique rain>: ripple-like)
* mud cracks : polygonal, V-shaped-supratidal, floodplain, playalake,
sabkhas.
③
기타
* swash marks : up-backwash on foreshore area
(Figure
3-35) : extensive, concave seaward
-
diagnostic indicator of shoreline(기울기에 따라 간격 달라짐)
* adhesion ripple : wind blowing sand over a wet substrate.
(eolian
환경)(3-36)
* pit and mound structure : volcano - shaped or pitlike by water/gas
escaping
* crystal impression : ice, halite, gypsum, pyrite in tidal flats,
sabkhas, lagoons
3)
Penecontemporaneous deformation structure
(1)
Load structure by mass of overlying sediment unit (coarse sand over mud)
* Load cast : flute caster 유사 but not distinct linear alignment,
no regular display
* Flame structure : mud intruding the overlying coarse unit
(2)
Ball and pillow structure : elliptical or pillow-shaped (pseudo-nodule)
by
slumping or downslope sliding(?)
(liquefaction
of the mud and mobilization of mud)
a
few centimeter ~ 1 meter
(3)
Dish structure : discountinuous, concave-upward laminations in sandstones
* dish and pillar - water escape structure
dewatering → columns or pillars of massive sands.
(upward
flow of water)
(4)
Convolute bedding : complex folding in mud or fine sand,
remarkable continuity of individual bed in convolute
unit
(slump structure 와 혼동
-
due to gravity only, soft sediment faulting 와 함께 발생)
→
(liquefaction, turbidite 층에서 많이 산출)
(5)
Slump structure : rapid sedimentation + slope instability
complicated, toothpaste-type folding w/
overturned folds and faults
from glacial, point bar, dune, delta, tidal flats turbidite
(6)
injection structure : a few cm ~ several m
sandstone
sill - concordant ┐ by liquefaction + loading
sandstone
dike - discordant ┘
(jnjection from mostly below, some above)