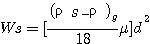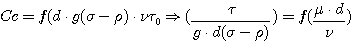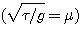| 제 3 장. Sedimentary Processes |
|
- Fluid : gas, liquid - Shear force : stress(pressure) parallel to the surface - Body force : gravity, inertia - Dynamic viscosity (μ)mju : coefficient of the shear to its rate of shear (=molecular viscosity) : 분자간 작용하는 힘 (두 판사이의 얇은 film layer가 가지는 tangential force) -
Kinematic viscosity (ν)nu = Laminar flow : Re < 0.1 ┐ normally Re 〈 2000 Turbulent flow : Re ~ 1000 ┘ Re 〉 2000 - Fr : Fr 〈 1 : tranquil flow . wave can not pass upstream (subcritical flow) Fr 〉 1 : rapid flow . wave can not pass upstream (supercritical flow) - Hjulstrom's diagram - Hydraulic sortion - sliding, rolling, saltation, intermittent suspension or continuous suspension - Hydraulic equivalence : depending on intensity of the flow - Competence - Capacity
|
|
1.Biological Processes 1) degradation : 미생물에 의한 다른 생물체의 crushing, scraping, site reduction caused by consumption, burrowing, boring (해삼, gastropod, sea urchins, 소화)
2) pelletization : 배설에 의한 pellet - filter feeder, deposit feeder
3) organism - enhanced sedimentation sediment baffles → energy 감쇠 (marine grass) sediment trapper → blue green algae → stromatolites |
|
2.Physical Processes 1) Fluid flow ┌ Turbulent, laminar └ Rapid, tranquil force per unit area (pressure) : normal to surface : gravity stress(shear) : parallel to surface Shear Stress : maximum at base (τ) zero at free surface
Renold
number : (1883, 1884 : 영국수학자) ν(nu) : Kinematic viscosity η(eta) : morecular viscosity ρ : density μ : viscosity U : velocity L : unit length (pipe diameter) (mean flow depth)
* Open channel에서 ┌ Re 〉 2000 : tubulent flow (turbulent eddies) └ Re 〈 2000 : laminar
* Flow 내에 towing sphere가 있을 때 Re = 24 → eddies in the wake Re 〈 1 : under laminar flow
Froude number : 영국조선설계사 Fr
= U=관성 (유속), D=depth of water, g=gravity acceleration ┌ Fr 〈 1.0 : tranquil or subcritical └ Fr 〉 1.0 : supercritical, rapid flow
* boundary layer : zone of shear stress
thicker - turbulent
* flow separation : Figure 2-6
* flow (natural current)의 구분
┌ Steady : 일정한 지점에서만 flow velosity (방향 속도) 가 일정 (하류 방향은 속도 감소) └ unsteady : 일정만 지점에서만 flow velocity 가 일정하지 않음 (river →계절) ┌ uniform : 흐르는 방향을 따라 속도가 항상 같음 (streamline 이 평행) └ non - uniform : 흐르는 방향을 따라 속도가 항상 다름 (강굽이에서 처럼) streamline : flow 의 세기 방향의 변화를 묘사 ( 밀집 → velocity 증가)
2) Settling of particles
Stoke's law : for single particle
WS : settling velocity d : diameter ρs-ρ : density difference μ : viscosity
* effect of shape ⇒ equivalent diamater (ex : shell)
3) Sediment entertainment : threshold velocity - 임계속도 for moving Hjulstrom diagram : clay, silt size grain의 침식 이동이 fine sand 에 비해 어려움
Cc : 임계조건 d : 입도 g(σ-ρ)
: 잠수중력 τo : shear stress ν : kinematic viscosity f : Reynold 수
* grain movement - two mechanism : ① fluid drag on grains in contact with fluid ② hydrodynamic lift force - 방해 요소: 입자의 무게, 입자간 점착력 - motion type: ① traction - slide, roll ┐ bed load ② saltation - hop, boune ┘ ③ suspended or wash load
Mississippi 전세계 뜬짐 65% 300억t 녹은짐 29% 36억t 밑짐 6% 30억t
4) Hydraulics and sediment texture
hydraulic sorting, abrasion - Competence - 일정한 유속의 유체가 운반할 수 있는 최대 입자 크기 - Capacity: 일정 유체가 운반 가능한 퇴적물 총량
Saltation population : 90~95% 의 총 bedload (figure 2-9)
*입자모양 : flow에 가장 적은 저항을 갖는 자세로 퇴적 |
|
3.Bedforms * Flow regime : fluid flow, bed configuration, dissipation of energy, phase(bed and water surface) 의 관계들의 총체로서 표현
Upper flow regime Fr 〉1.0 Lower flow regime Fr 〈 1.0
* ripple → sand wave → megaripple(dune) → plane(flat) bed → antidune → chutes and pools ----------------Lower F. R..------------╂------------ Upper F. R..---------------------
* bedform은 turbulence of flow와 grain 의 interaction에 의해 형성 (flow power :: product of velocity(V) × boundary shear stress(τo)) Figure 2-9, 2-10, 2-11 참조 |
|
4.Sediment gravity processes (mass flow) ⓐ turbidity current : density currents - turbidite ⓑ liquified sediment flow : upward flowing 에 의해 supporting ⓒ grain flow : grain to grain collision: dry grain flow ⓓ debris flow : mixtune of fine coarse -matrix strength & buoyancy ⓔ slump/slide
Figure 2-14 참조 |
|
5.Tides and tidal currents)
┌ spring tide : 사리 └ neep tide : 조금
micro tidal range : 〈 2m meso tidal range : 2-4m macro tidal range : 〉4m
* unequal high and low tidal velocity - currents └→ time - velocity asymmetry ┌ flood slack : 만조 └ ebb slack : 저조
* maximum flood tidal current : after mid tide maximum ebb tidal current : near low tide flood-dominated or ebb-dominated |
|
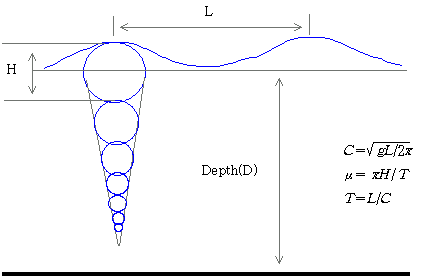
6. Waves
Surface wave = gravity wave → height period
┌ sea wave └ swell wave f(W.F.D) W : wind velocity D : duration of wind F : fetch, distance of water surface surf : mean coast * water motion in waves
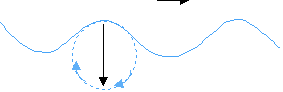
ordital motion : effective depth = 1/2 of wavelength * longshore current : parallel to shore * rip current : after breaking surf : back-flowing currents |
|
제1장. 퇴적물 및 퇴적암의 일반적인 성질 |

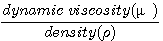
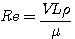 =
= 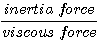
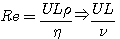
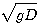
 → downstream (velocity increase)
→ downstream (velocity increase)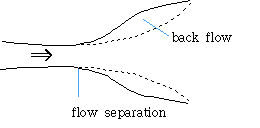 change in diameter
change in diameter